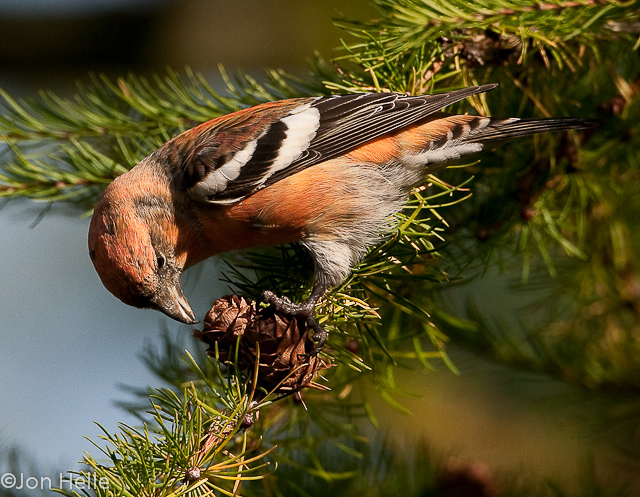
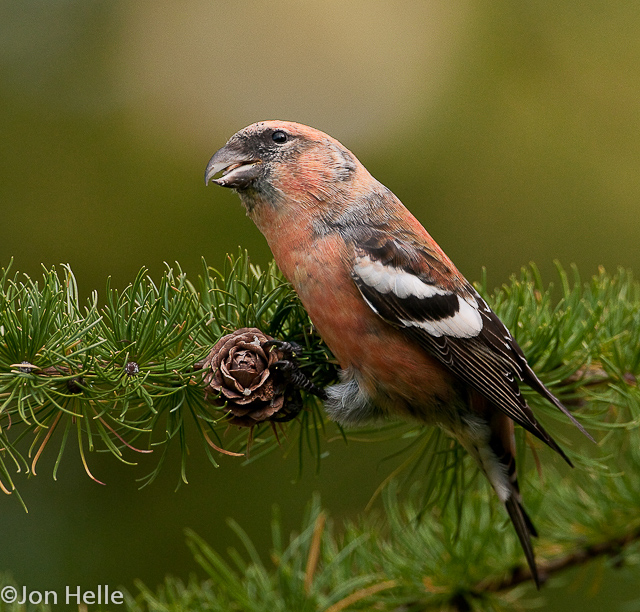
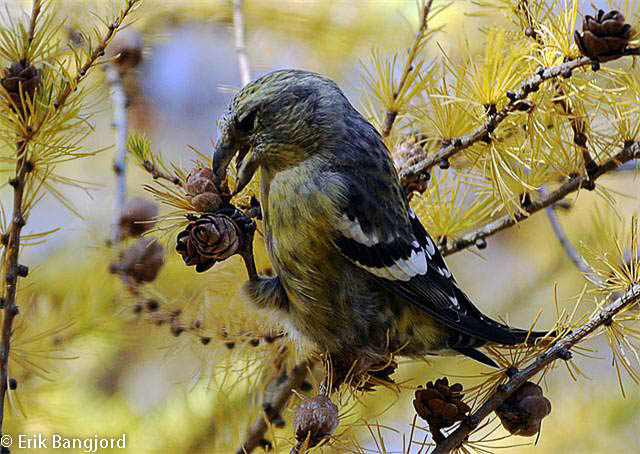
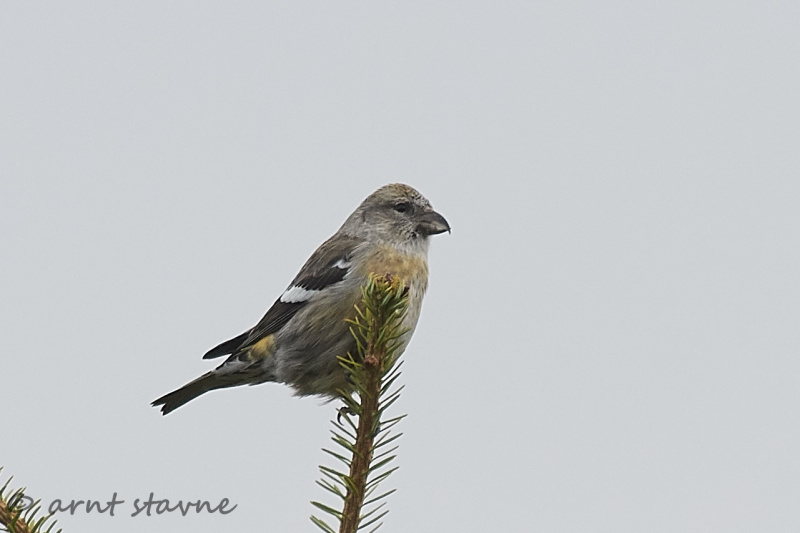
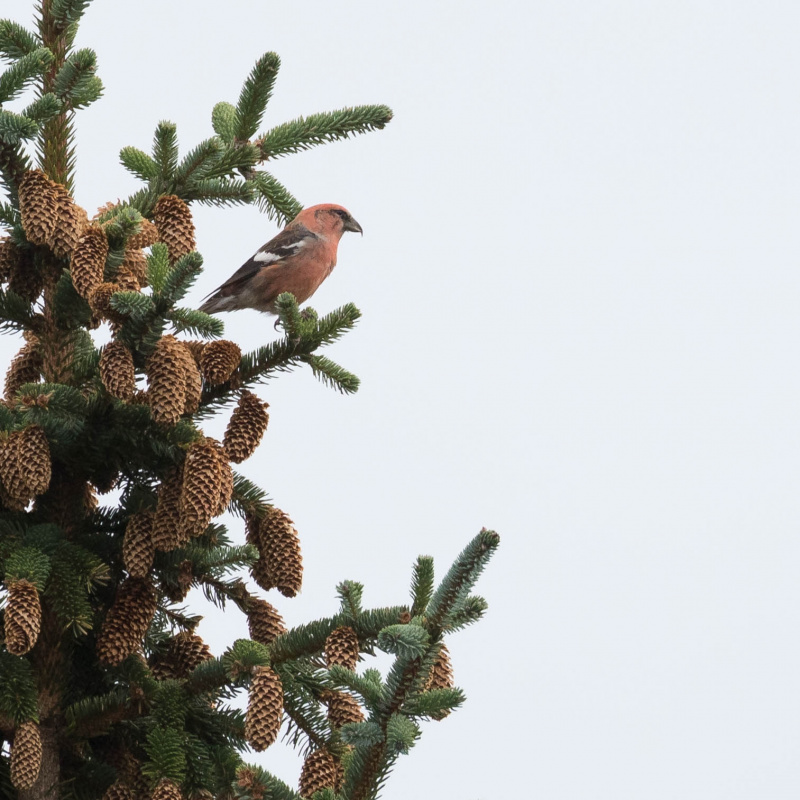
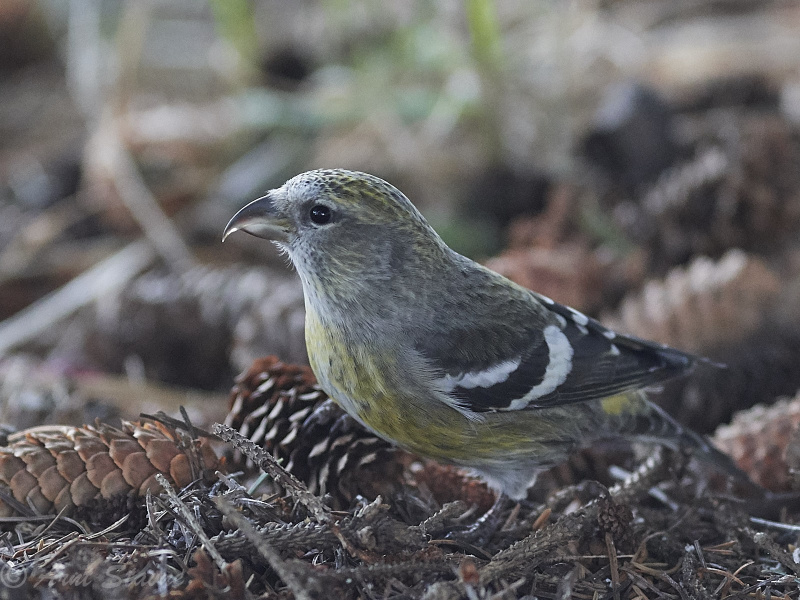
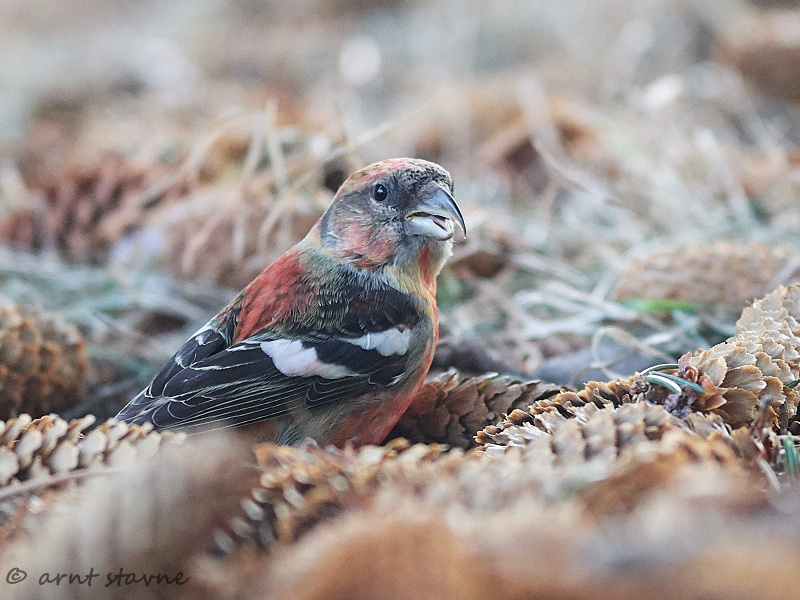
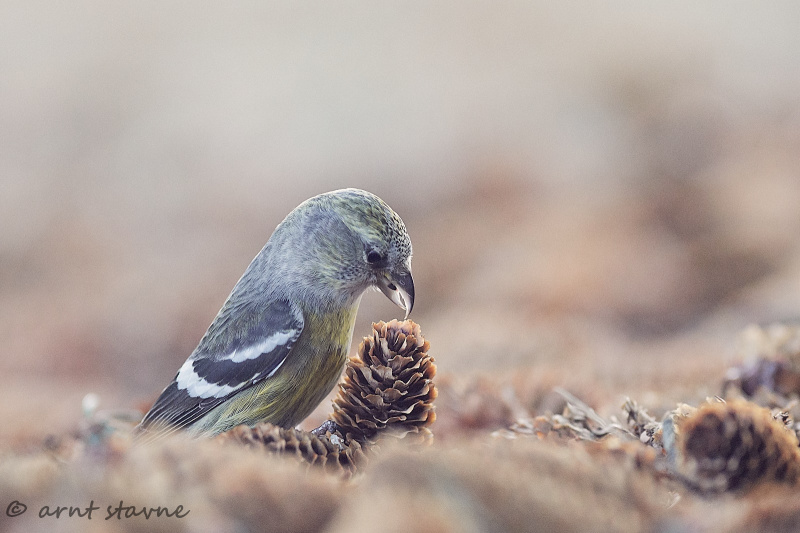
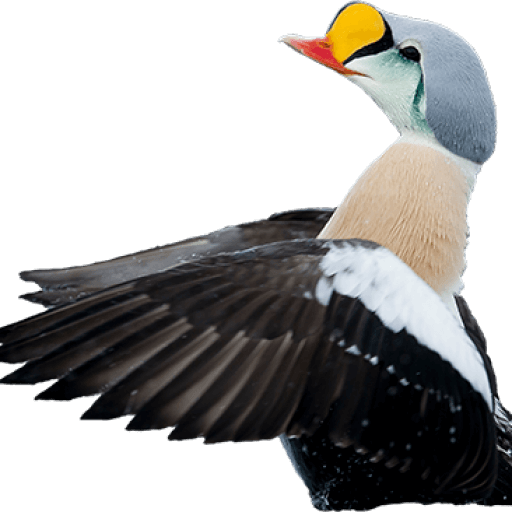
Two-barred Crossbill (Loxia leucoptera)
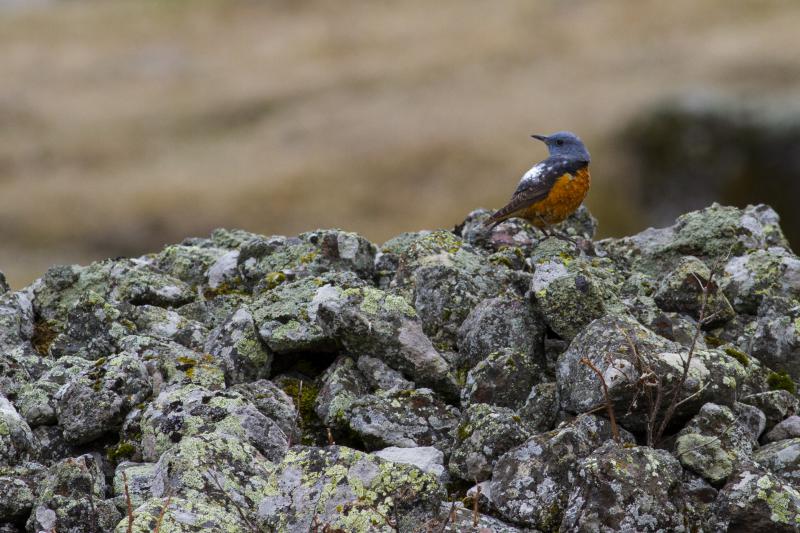
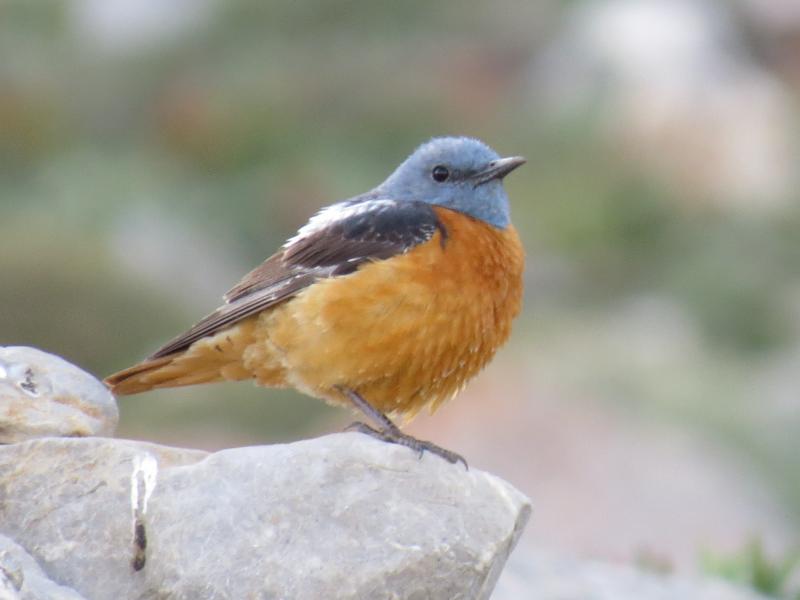
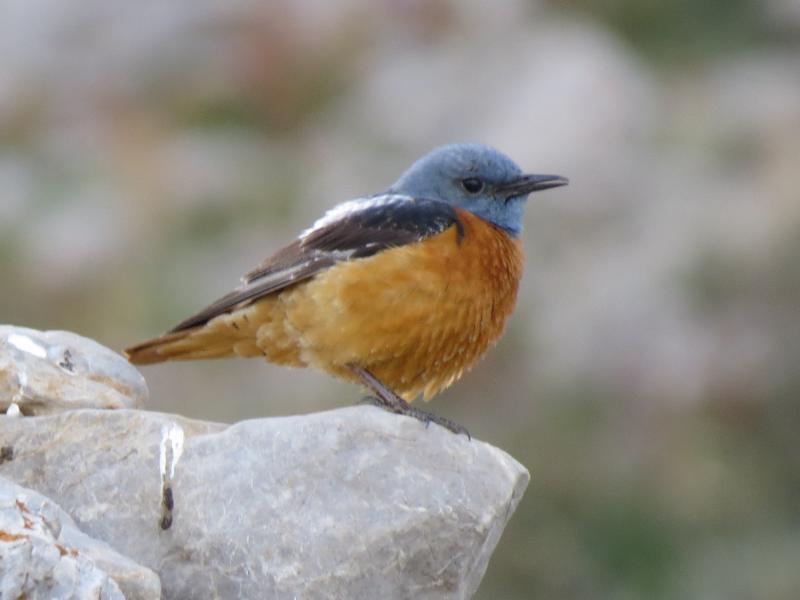
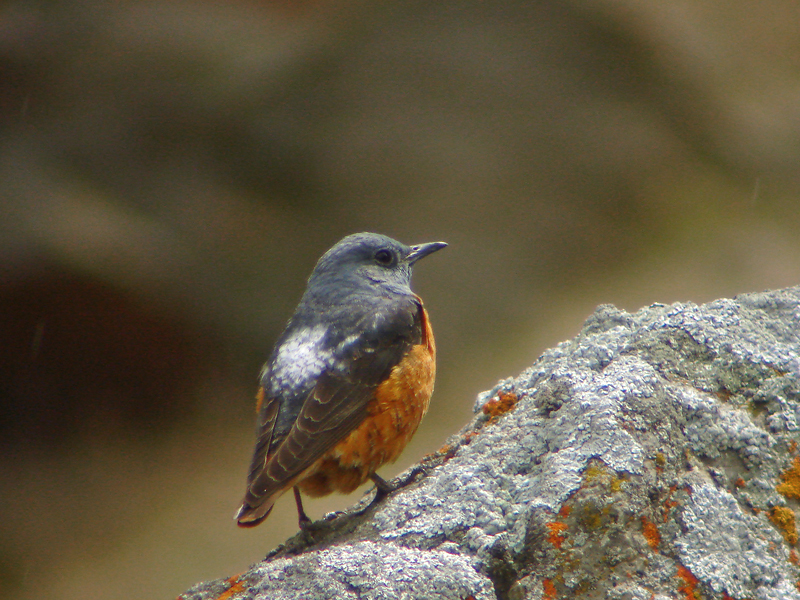
Rufous-tailed Rock-thrush (Monticola saxatilis)
Plumage like other crossbills; male red, female and juveniles green. Both sexes and all ages with two broad, white wing-bars, which distinguishes it from congeners. Nonetheless, the species is easily overlooked when in mixed flocks with other crossbills. Build slightly more slender and long-tailed than other crossbills. Often discovered through its contact call.
Sound:Contact call a "chep chep" similar to crossbill but softer, interspersed with characteristic, toy-trumpet call with redpoll-like timbre, but with a more flat intonation. Song more like redpoll than a crossbill, with rattling and chittering notes.
Calls:
Distribution:
Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCSounds: Recorded by Patrick Åberg,http://www.xeno-canto.org/ ,CC license
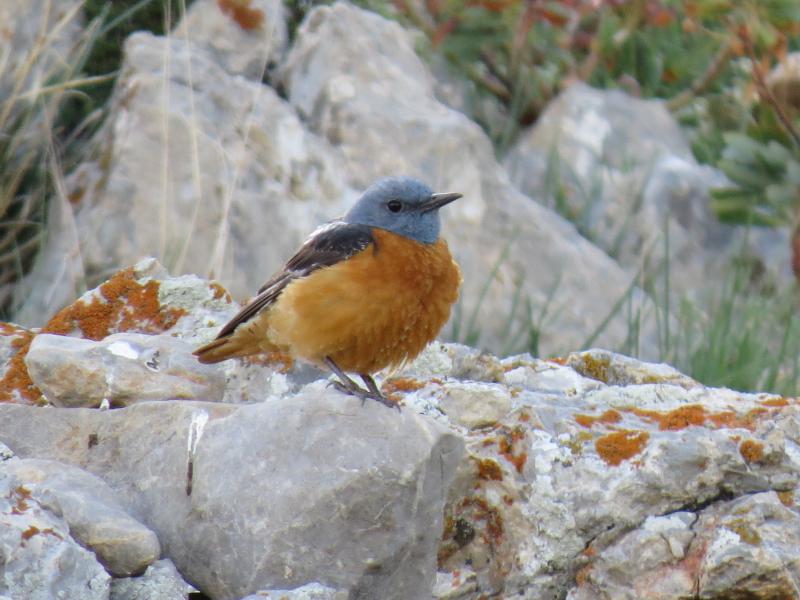
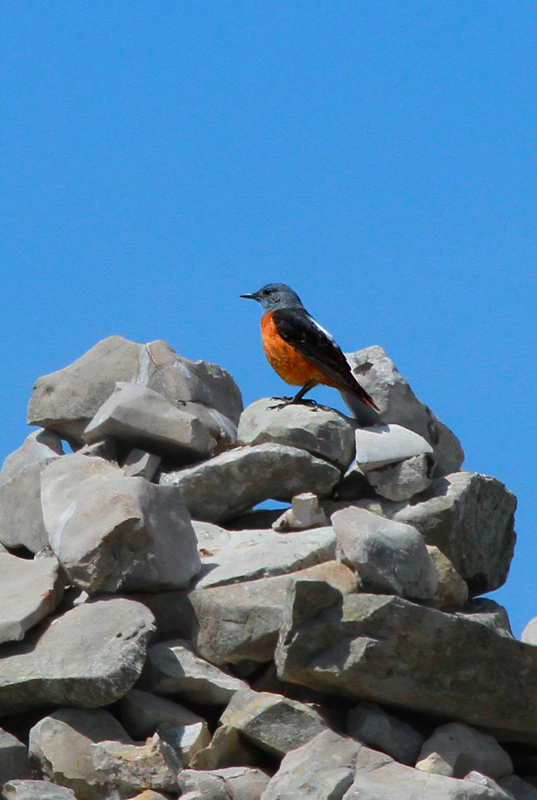
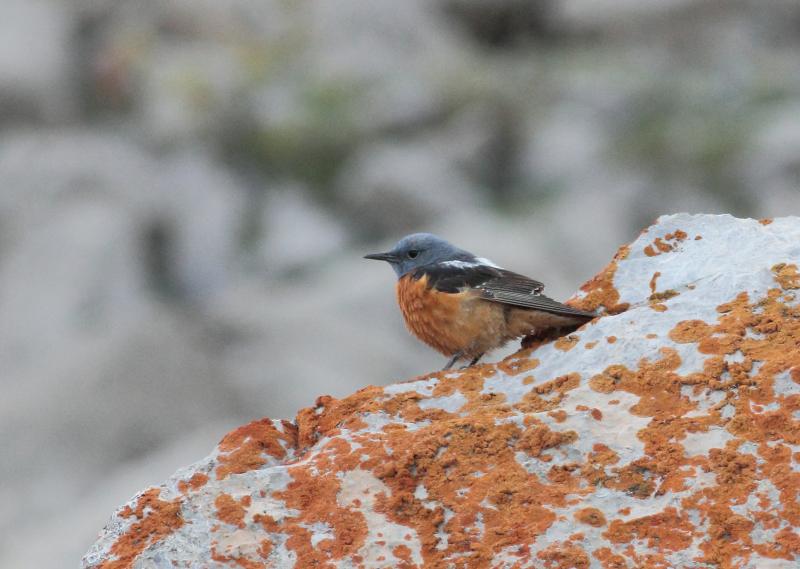
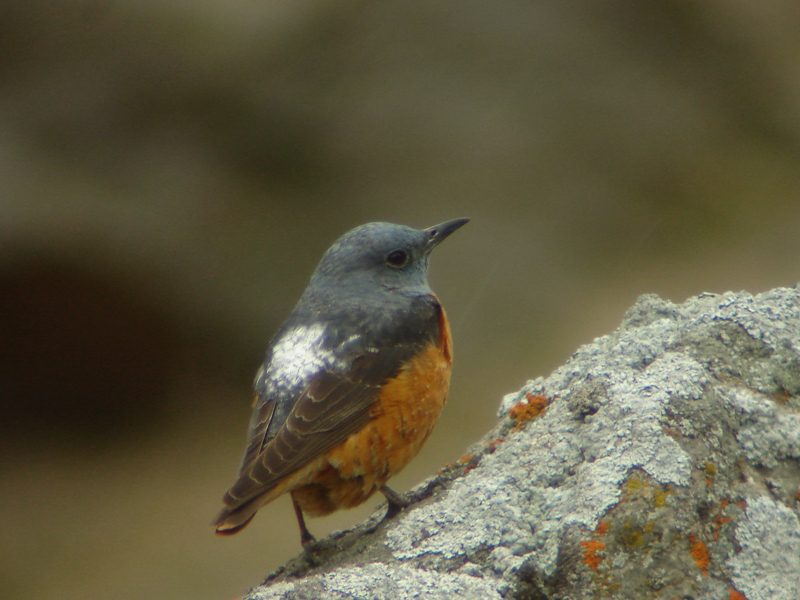
Compact built bird attached to rocky habitat. Differs in all plumages from Blue Rock-thrush, Monticola solitarius by short, rufous tail and shorter bill. Primary projection very long, and wing-tips almost reaches end of tail in perching birds. Male in breeding plumage unmistakable with blue-grey head, orange-buff underparts and white patch on back (variable). Male resembles female and immature birds when not in breeding plumage, but can sometimes be sexed by partly grey head and hints of white on back. General characteristics of non-breeding plumage are greyish brown and speckled upperparts, and orange-buff, vermiculated underparts. Then told from female Blue Rock-thrush by aforementioned different build, bill and tail, and also by paler throat-sides/breast and warmer rufous flanks. Posture usually upright with giss resembling more a wheatear than a thrush.
Sound:Alarm call a soft, wheatear-like "peeu", often accompanied by harder "tek" calls. Also a very nasal, drawn-out wheeze. Song varied and pleasing, and often very difficult to tell from Blue Rock-thrush. It is generally softer, more varied and the deeper notes are less tremulous and vibrating. A higher proportion of the song is in the higher register, with fewer lower fluting sounds, and more mimicry. Both sexes sing, but females less than males.
Song:
Distribution:
Xeno-canto: map
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCCC-photo:gilgit2, Licence,Link.

 English
English Albanian
Albanian
 Armenian
Armenian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Catalan
Catalan
 Croatian
Croatian
 Czech
Czech
 Danish
Danish
 Dutch
Dutch
 Finnish
Finnish
 French
French
 Georgian
Georgian
 German
German
 Greek
Greek
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Italian
Italian
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Macedonian
Macedonian
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Polish
Polish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Romanian
Romanian
 Russian
Russian
 Sami : Lule sami
Sami : Lule sami
 Sami : North sami
Sami : North sami
 Sami : South sami
Sami : South sami
 Scientific names
Scientific names
 Serbian
Serbian
 Spanish
Spanish
 Swedish
Swedish
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian