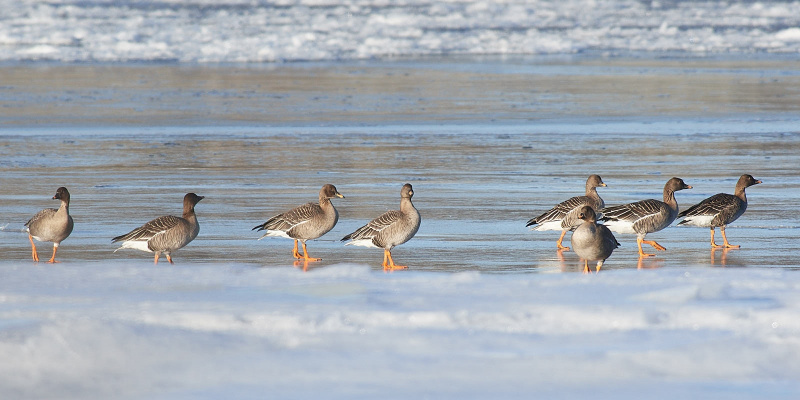
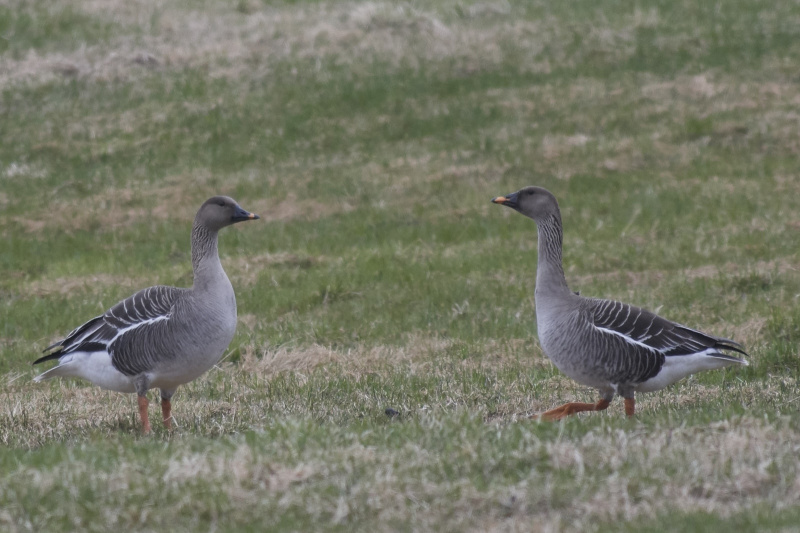
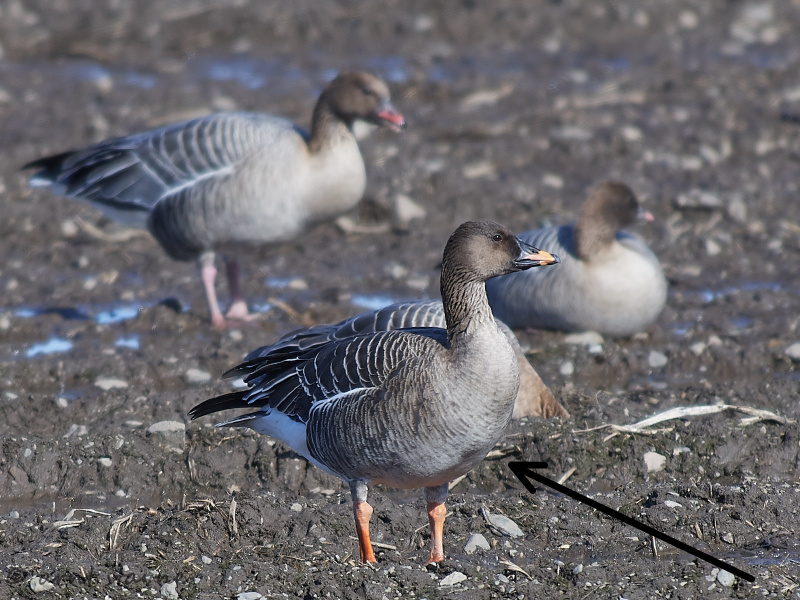
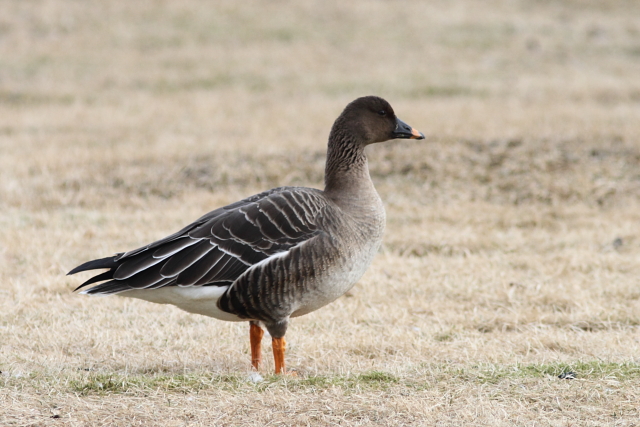
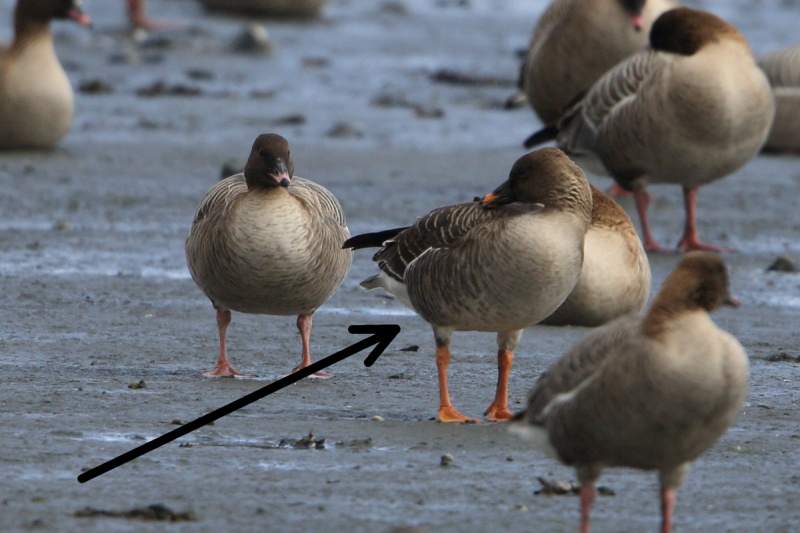
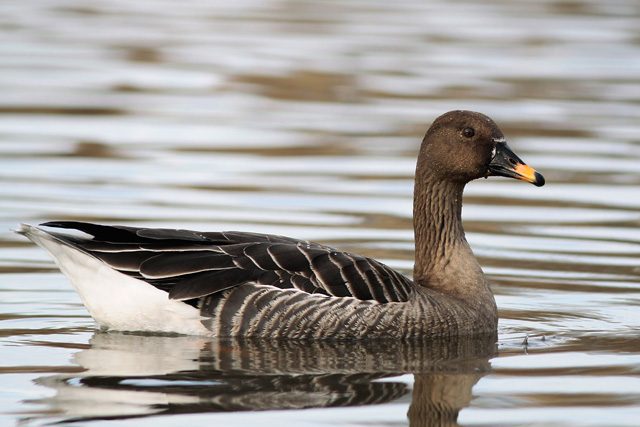
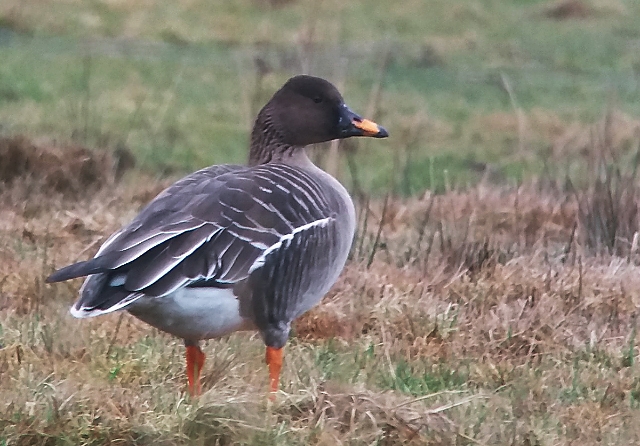
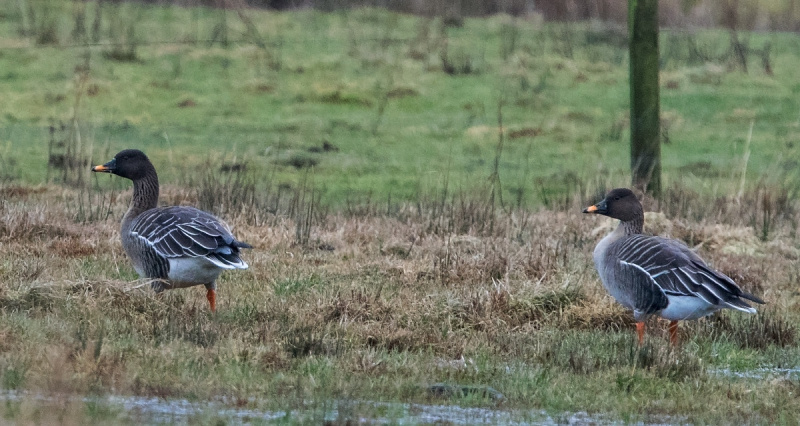
Bean Goose (Anser fabalis)
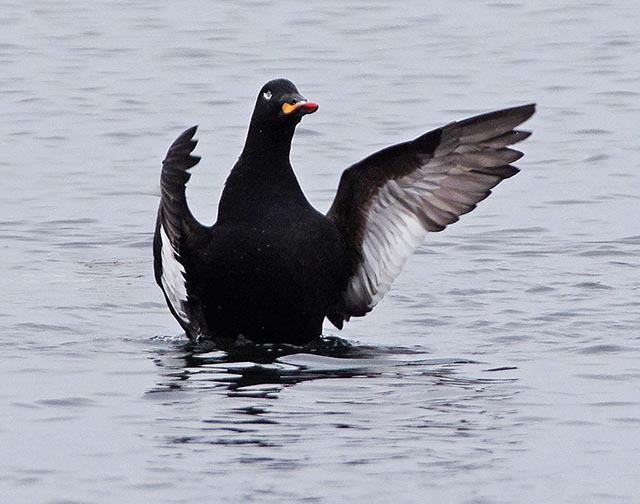
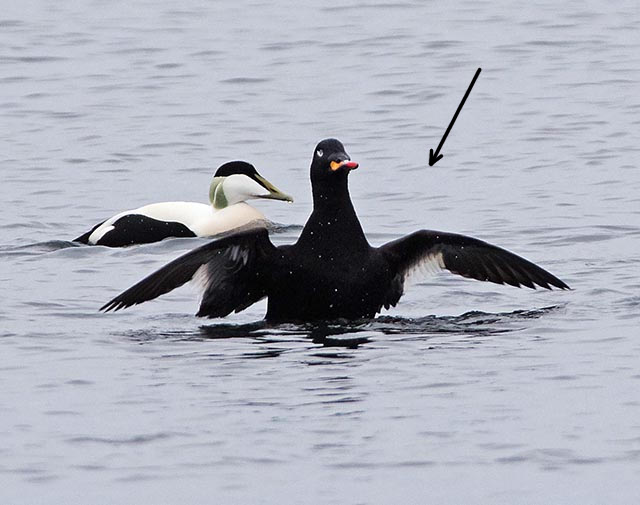
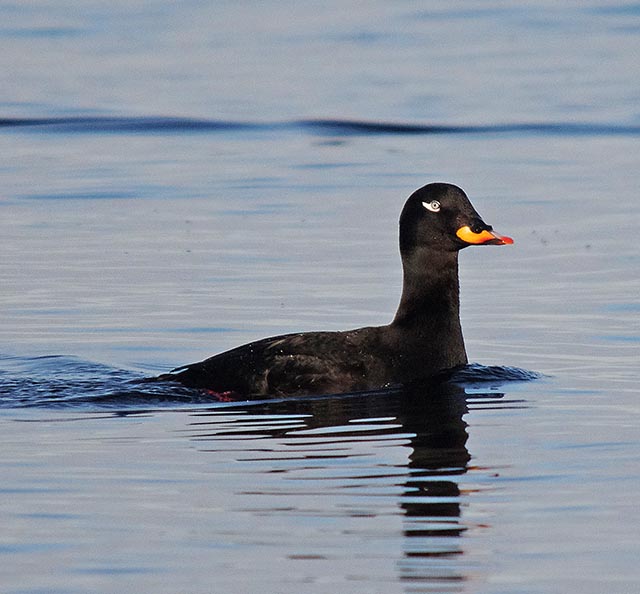
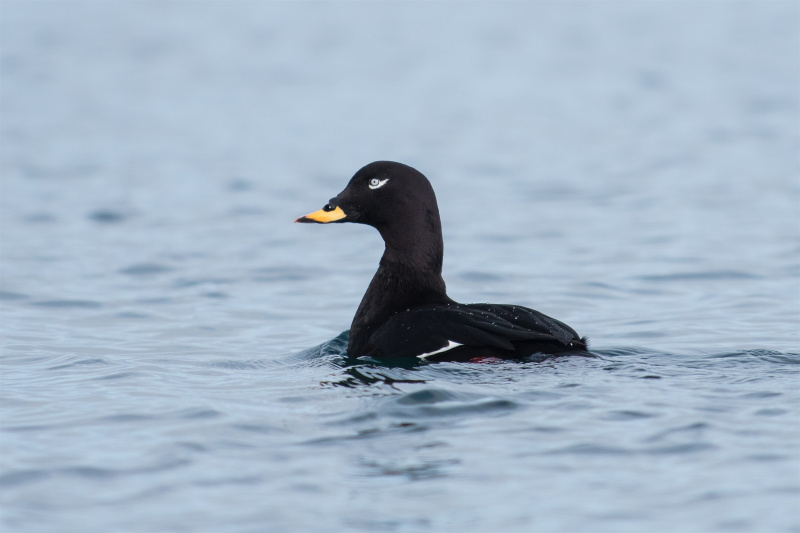
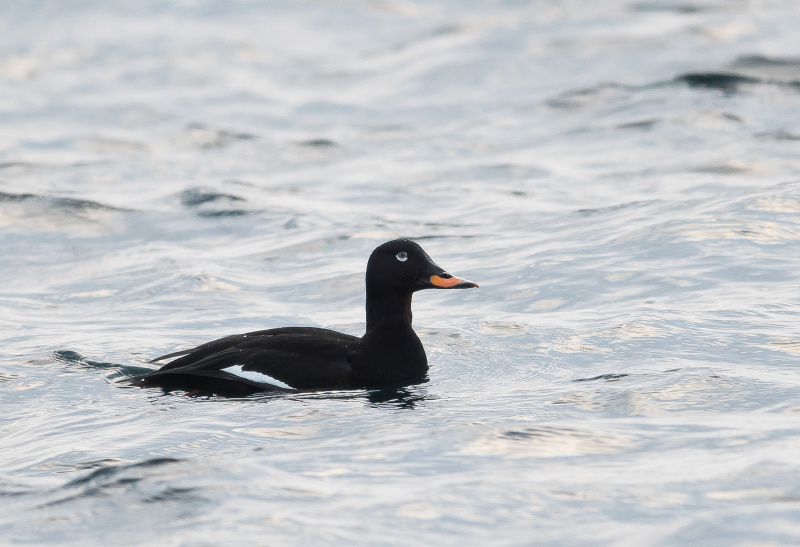
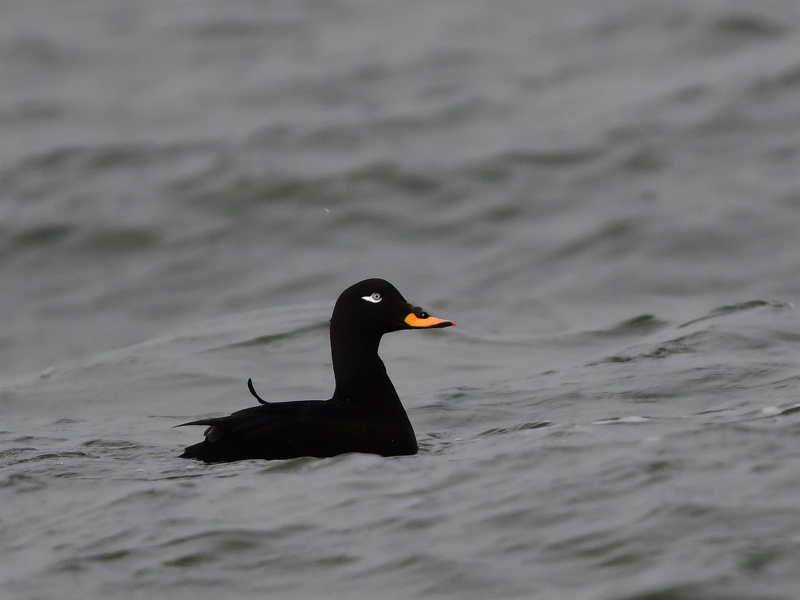
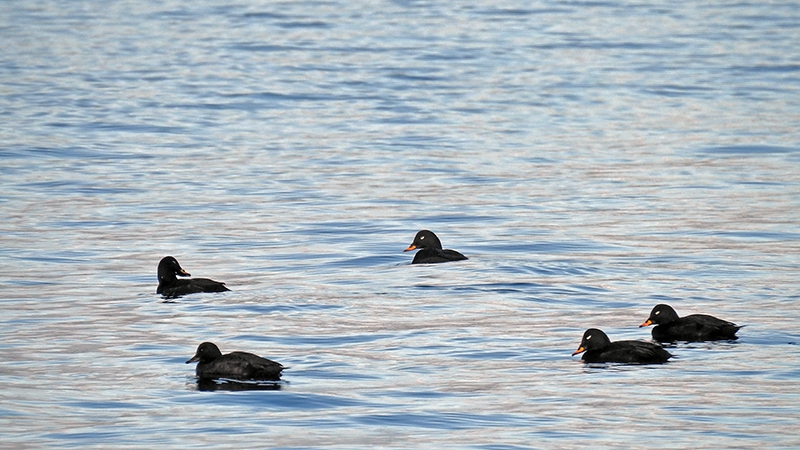
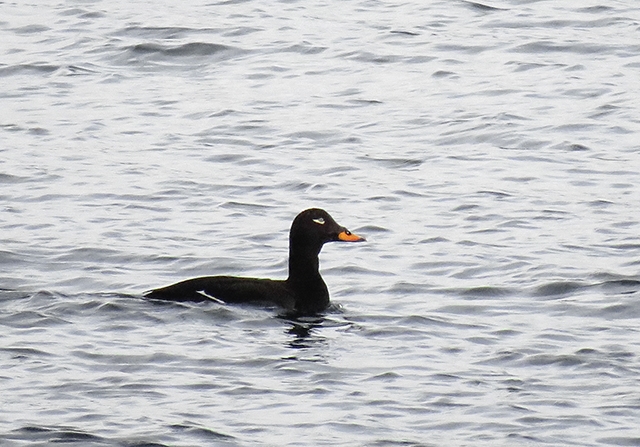
Velvet Scoter (Melanitta fusca)
Orange legs, black and orange bill. Differs from juvenile White-fronted Goose by less contrast between cheeks and base of bill and crown, more prominent pale edges on back feathers, and by bill colour. Has much darker back than Pink-footed Goose (and never greyish). Colour of legs and bill can be surprisingly difficult to judge in unfavourable light. 2 subspecies that may be considered separate species in near future: A.f.rossicus has shorter bill with more extensive black markings than A.f.fabalis.
Sound:Do not call as much as other grey geese. Sounds similar to the lower sounds of Pink-footed goose, with various reedy calls, but harder, less nasal and more of a "sore throat".
Contact call:
Distribution:
Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCSounds:Recorded by Jens Kirkeby, http://www.xeno-canto.org ,CC license
White secondaries the most striking feature in all plumages. Generally heavy built with large bill, heavy head, thick neck and short tail. Male: black with white crescent below eye and partly orange bill. Female sooty black with variable light patches at lore and cheek. Flaps it's wings with a raised head when on water. Dives without jumping and with wings slightly open. Swimming birds may not always show white secondaries. Tends to form less dense flocks than Common Scoter, often with birds in single file.
Sound:Seldom heard. Calls: Short accented "tup tup tup" and a shivering "gahhahahaha".
Distribution:Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CC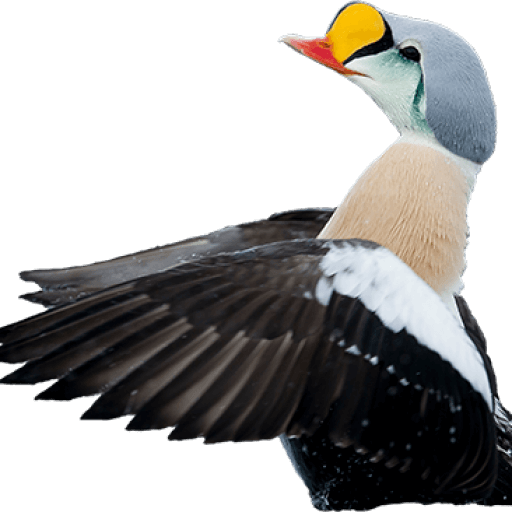
 English
English Albanian
Albanian
 Armenian
Armenian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Catalan
Catalan
 Croatian
Croatian
 Czech
Czech
 Danish
Danish
 Dutch
Dutch
 Finnish
Finnish
 French
French
 Georgian
Georgian
 German
German
 Greek
Greek
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Italian
Italian
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Macedonian
Macedonian
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Polish
Polish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Romanian
Romanian
 Russian
Russian
 Sami : Lule sami
Sami : Lule sami
 Sami : North sami
Sami : North sami
 Sami : South sami
Sami : South sami
 Scientific names
Scientific names
 Serbian
Serbian
 Spanish
Spanish
 Swedish
Swedish
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian