Pallid Swift (Apus pallidus)
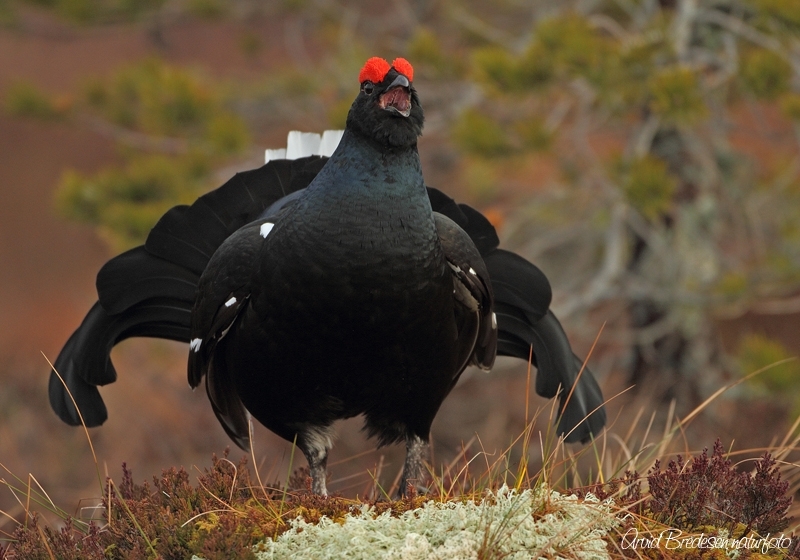
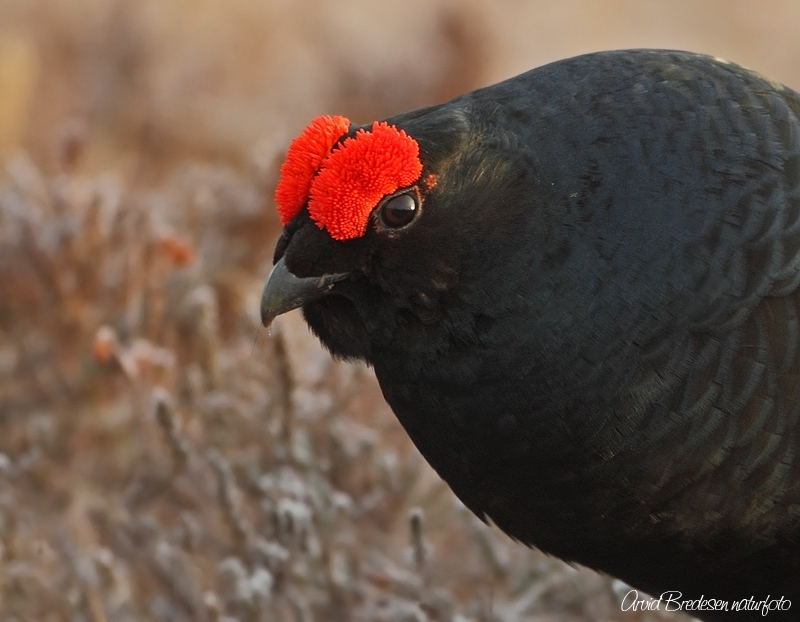
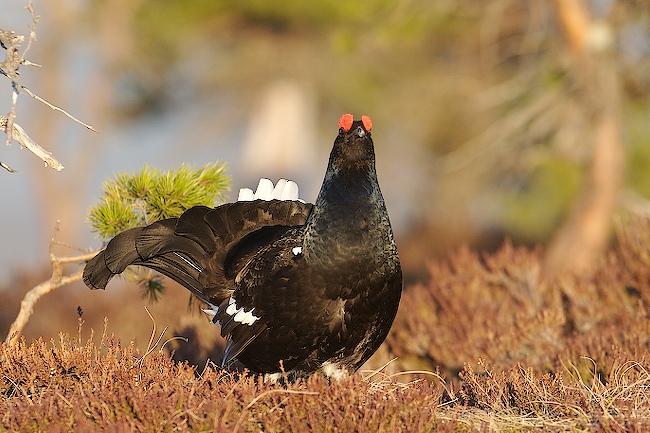
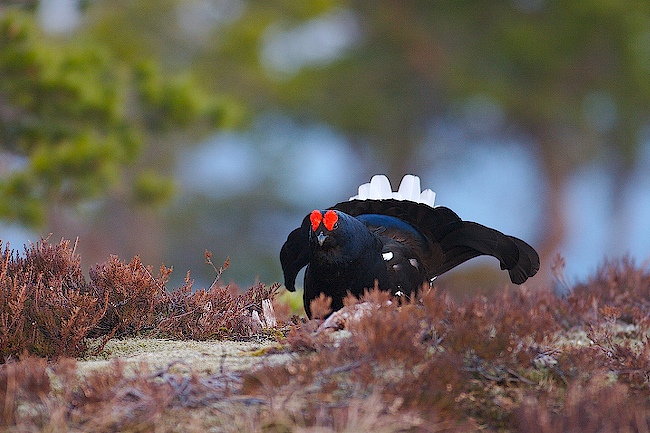
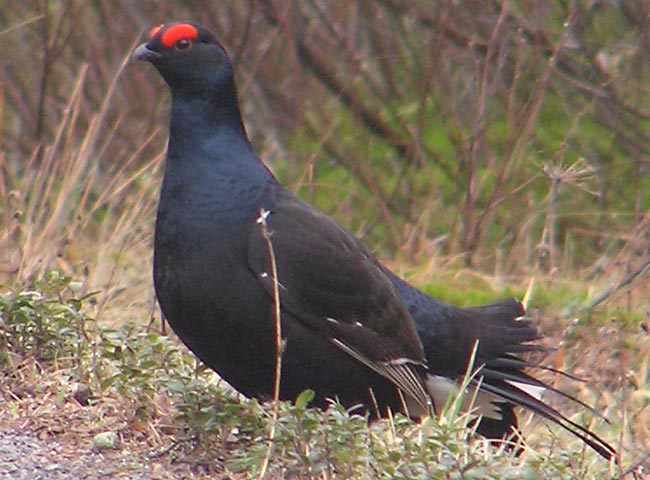
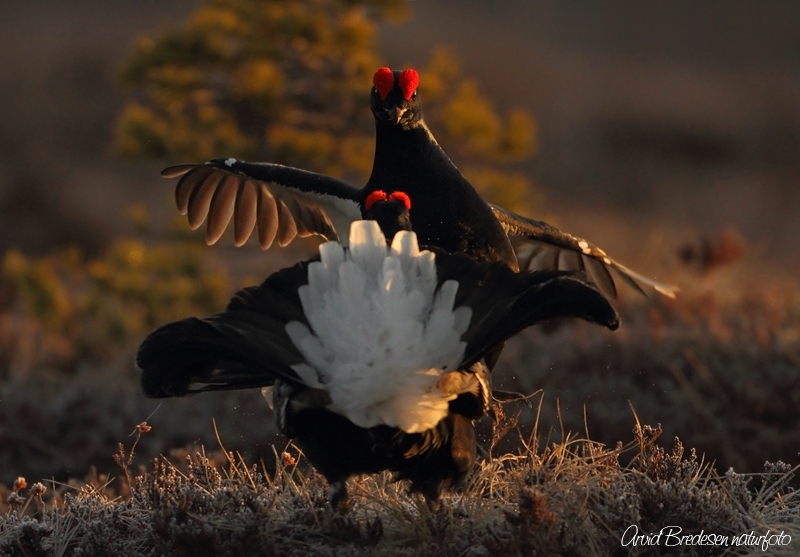
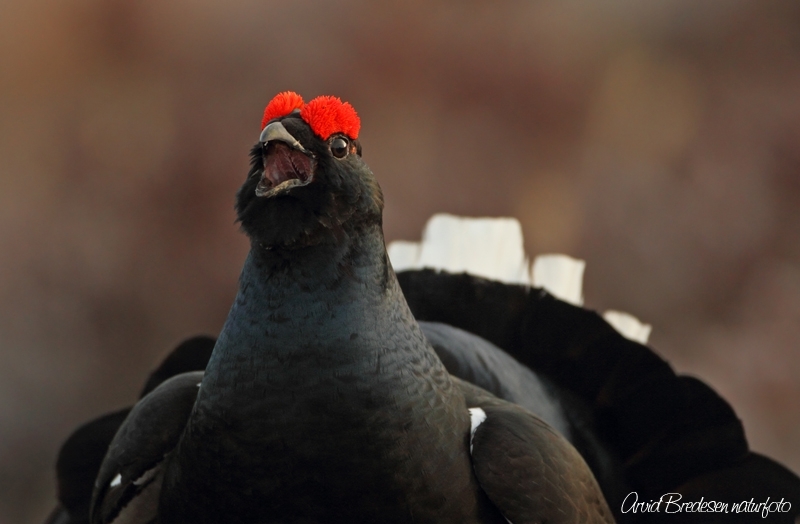
Black Grouse (Lyrurus tetrix)
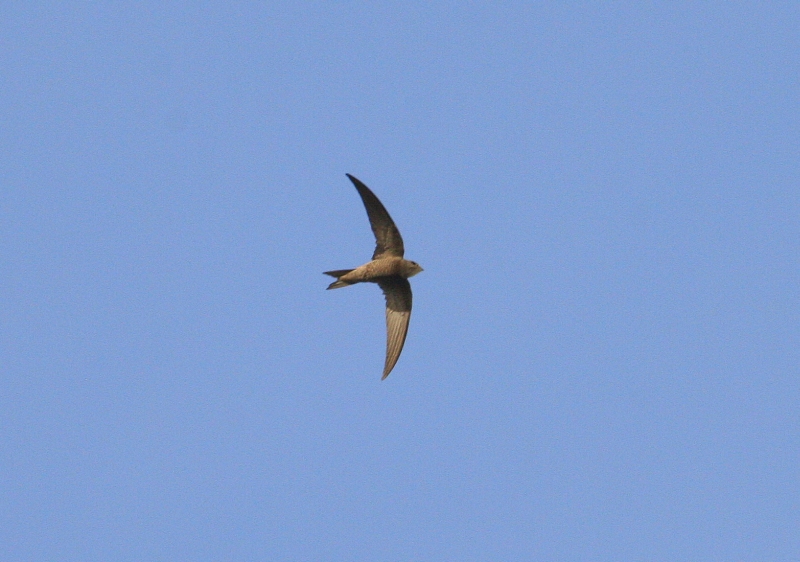
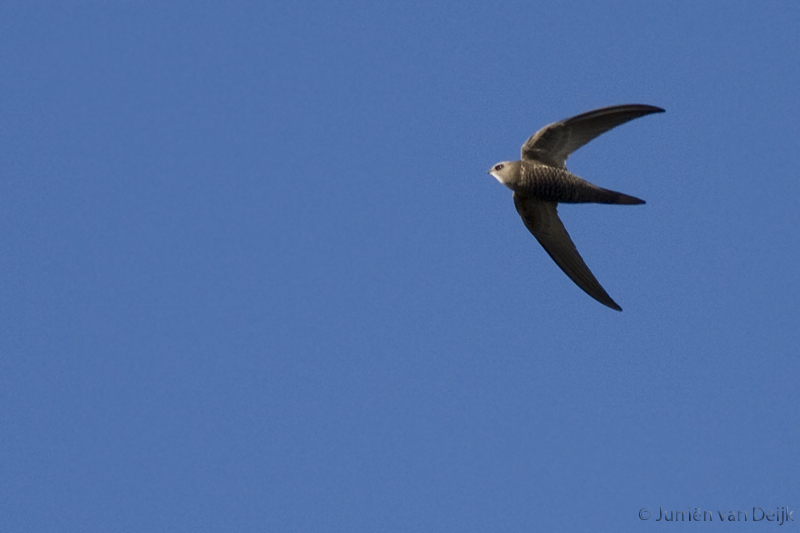
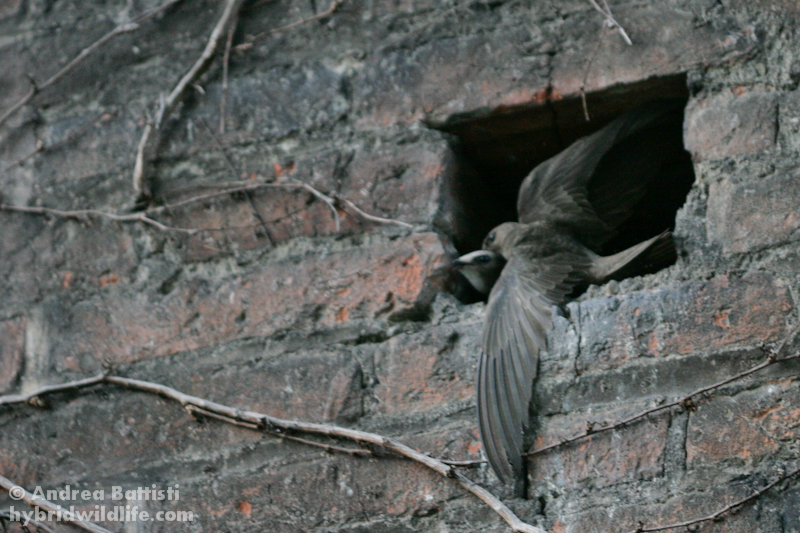
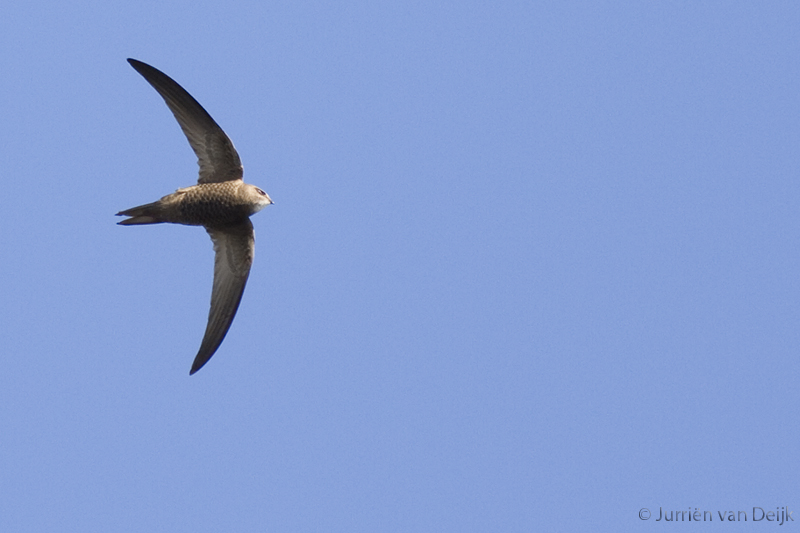
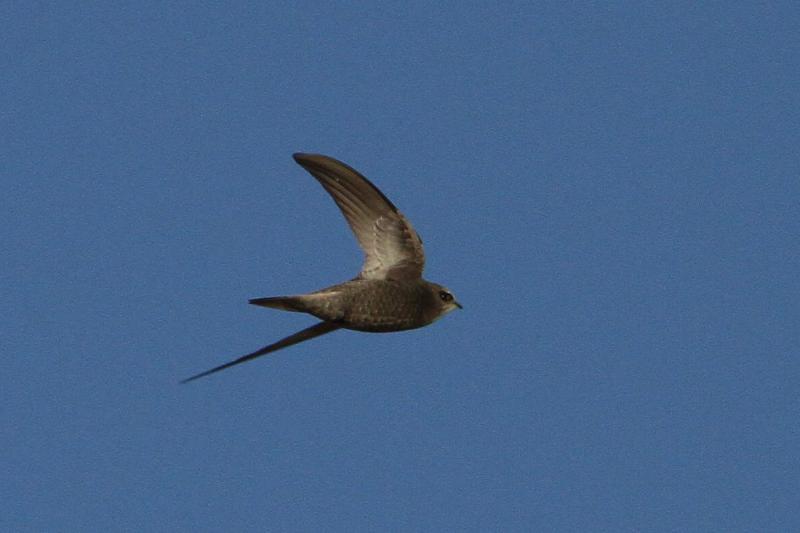
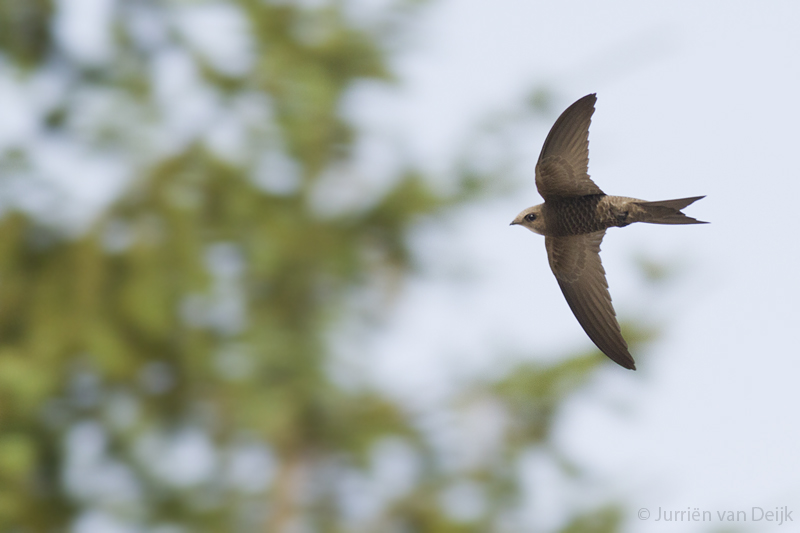
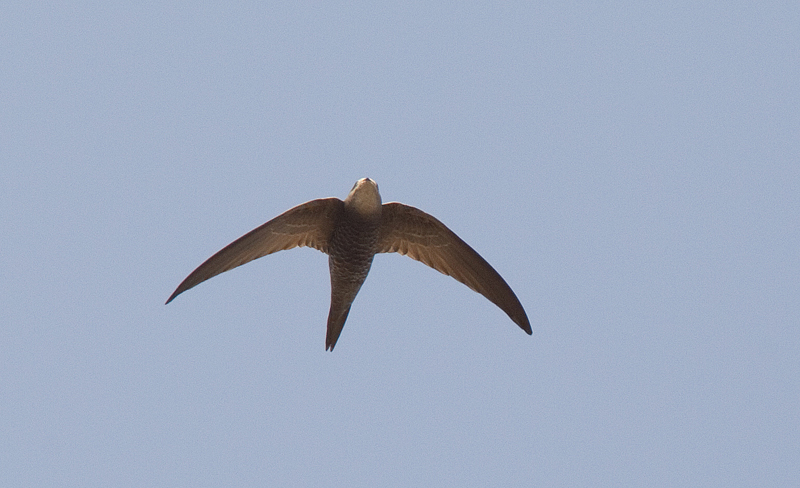
Very similar to Common Swift, and often difficult to identify in the field. Seeing the birds against a darker background, as opposed to the sky, brings out some of the characters more clearly. Generally paler and more sandy brown than Common Swift. Differs further from C. Swift by: Rounder wing tip (outermost primary shorter than the next), slightly broader wings, broader and flatter head. White throat patch bigger and more prominent. The face seems paler, which brings out the dark eye-mask. Back slightly darker than upper part of wings. More contrast between outer and inner primaries. Underparts with more pronounced scaly pattern. Flight less acrobatic, with slightly slower wing-beats, more frequent gliding and much less twinkling turns.
Sound:Similar to Common Swift, but usually very helpful for ID. Almost di-syllabic, with marked accent on second syllable which rapidly drops in pitch, "srrrree-aah". Common swift has a more even call, with accents on first part, without the sudden pitch-drop.
Contact call:
Distribution:
Xeno-canto: map
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCSound recording:Creative Commons,www.xeno-canto.org,Carlos W.,http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Male differs from Capercaillie in smaller size, stockier build, curled outer tail-feathers and pure white under tail-coverts. Both sexes with white wing bars. Female more evenly speckled than Capercaillie, lacking brick coloured patches on breast an neck. Much less noisy when flushed than Capercaillie.
Sound:Song: a far reaching, continuous, bubbly cooing, occasionally interrupted by a hissing "chooo-eee". Female calls with a nasal "go-go-go-gooo", ending on a falling drawn-out note.
Song:
Distribution:
Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CC
 English
English Albanian
Albanian
 Armenian
Armenian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Catalan
Catalan
 Croatian
Croatian
 Czech
Czech
 Danish
Danish
 Dutch
Dutch
 Finnish
Finnish
 French
French
 Georgian
Georgian
 German
German
 Greek
Greek
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Italian
Italian
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Macedonian
Macedonian
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Polish
Polish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Romanian
Romanian
 Russian
Russian
 Sami : Lule sami
Sami : Lule sami
 Sami : North sami
Sami : North sami
 Sami : South sami
Sami : South sami
 Scientific names
Scientific names
 Serbian
Serbian
 Spanish
Spanish
 Swedish
Swedish
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian