Topography (Anatomy and explanation)
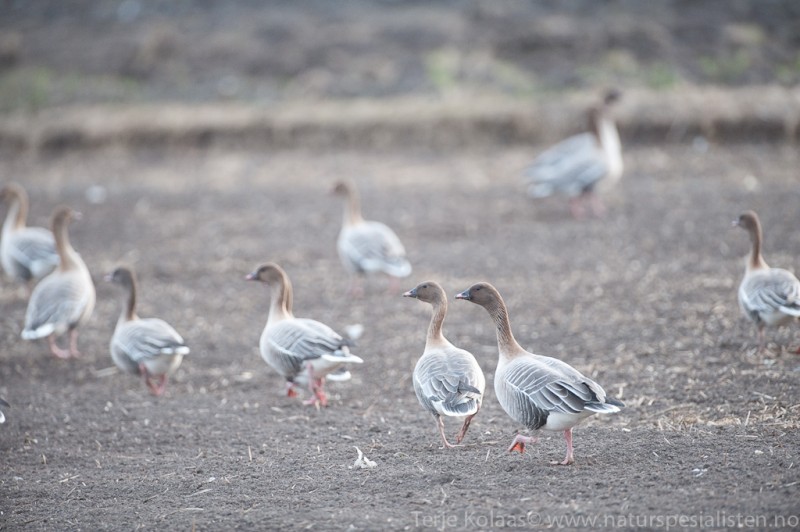
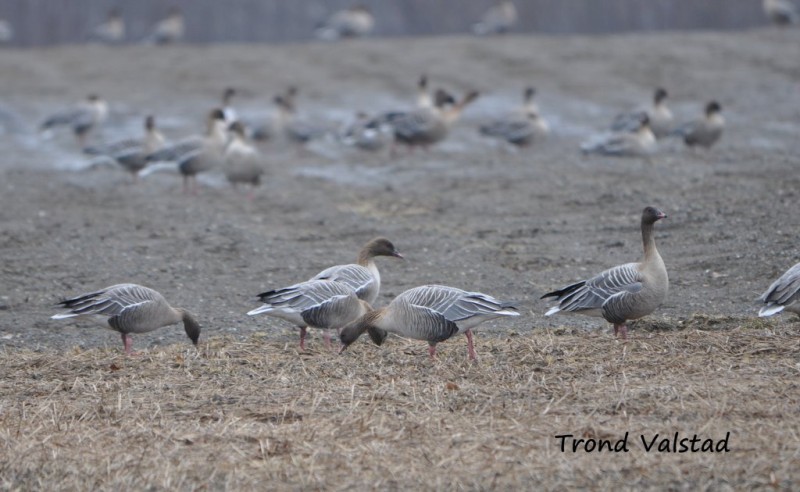
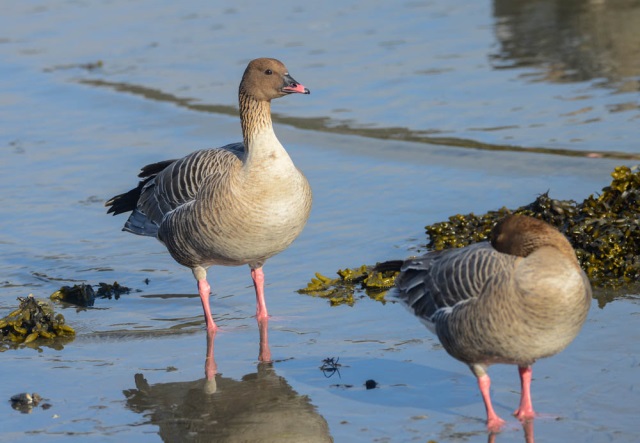
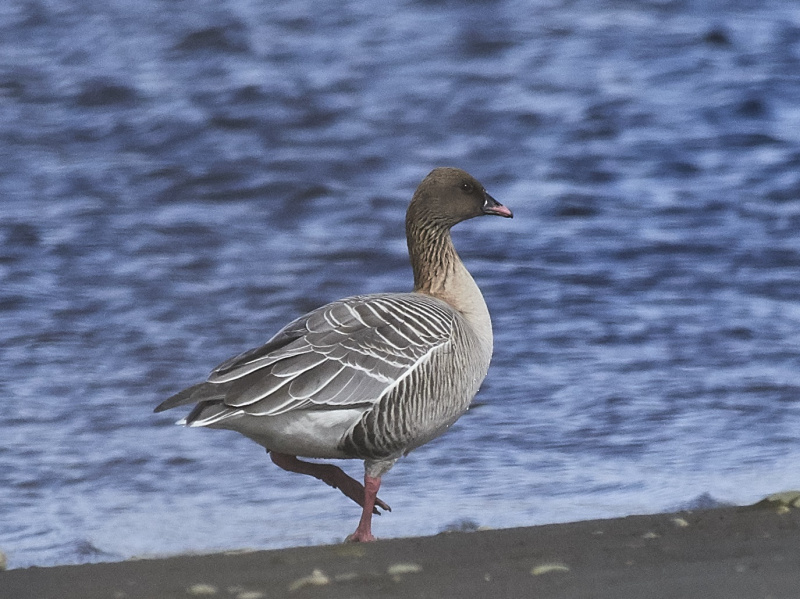
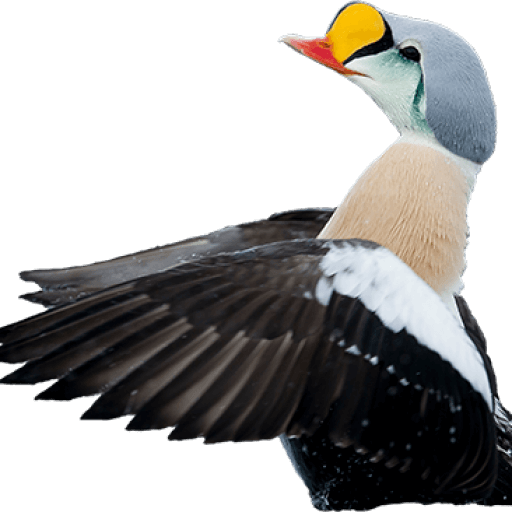
Pink-footed Goose (Anser brachyrhynchus)
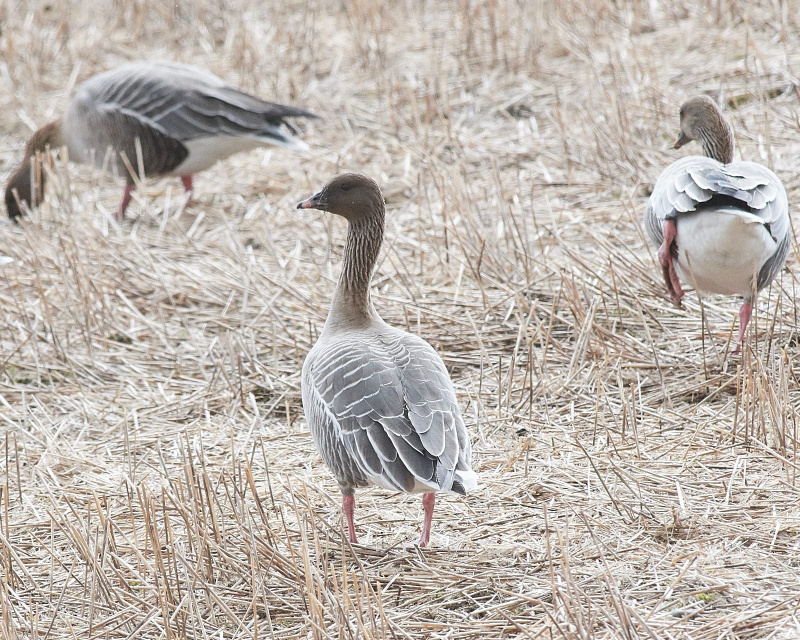
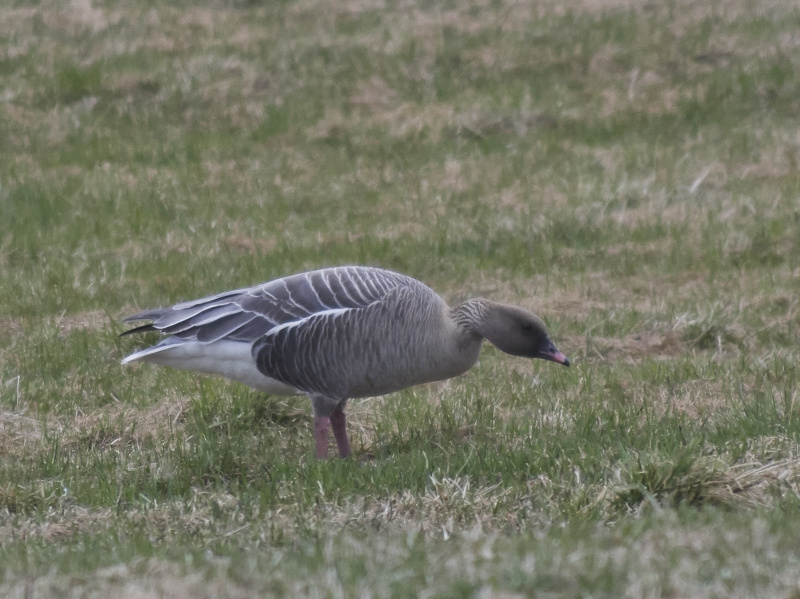
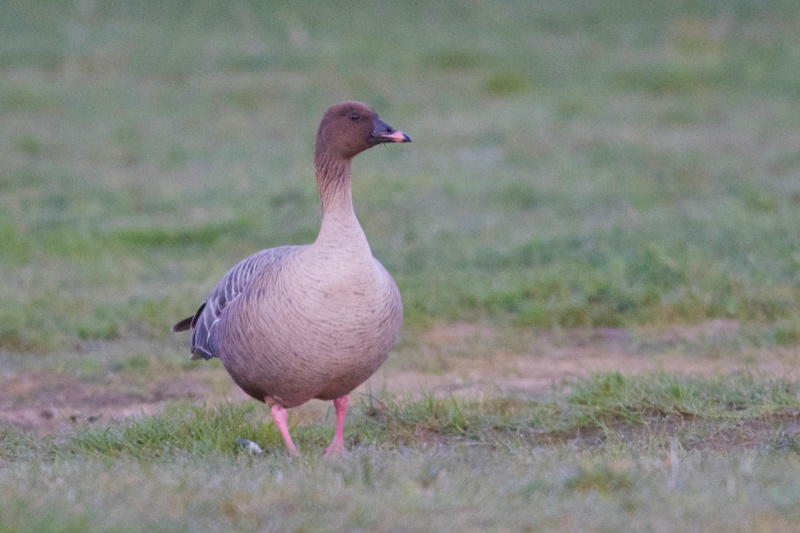
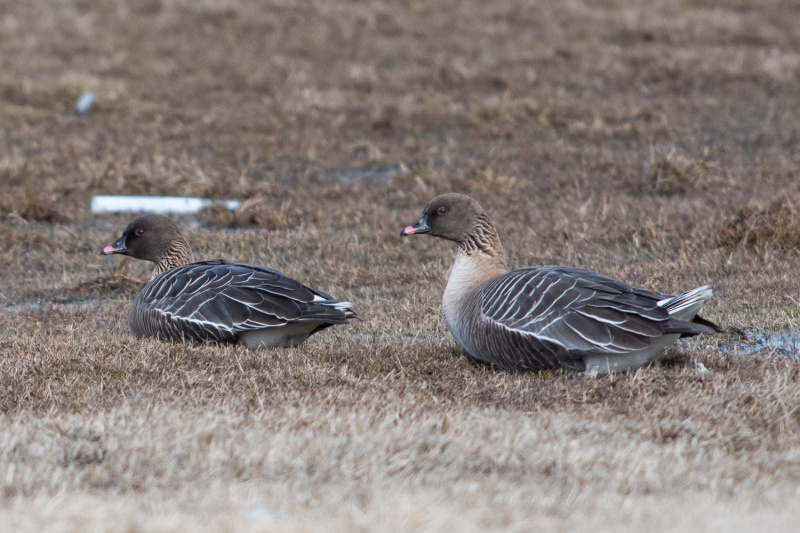
Description of main identification features in chosen species' appearance. Some bird anatomy terms are used, and it may be useful to study the photos above to learn them. All text written by Audun Eriksen.
Sound:Description of song and calls, and what to listen for in the audio files, and when learning the species. Some music terminology is used. Timbre: tone colour or tone quality. Ritardando: Tempo slowing down gradually. Register break: abrupt change in pitch due to sudden jump in resonating length of throat (typically in long-necked birds).
Distribution: Ecology:Link to webpage describing ecology and population of the species.
Links:
A collection of hyperlinks for each species can be found here. You can easily see latest observations, additional photos/sounds and watch videos of the species without having to search for the species name.
CCCreative Commons licenced photos and sounds are listed here with links. For media not listed, usage is permitted by direct appointment with copyright owner. See watermark on photos.
Pink bill and legs distinguishes it from Bean Goose. This can however be a deceiving character in poor light. Also differs from Bean Goose by pale grey,not brownish, upperparts. The darkest part of the body is the flanks (Bean Goose have equally dark flanks and back).
Sound:Similar to Bean Goose and White-fronted Goose, but more nasal and a little higher pitched than the first, and less musical and laughing than the second. Easily told from Greylag Goose by frequent nasal, high pitched "wink-wink".
Contact call:
Distribution:
Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCSounds:Recorded by Elias A. Ryberg,http://www.xeno-canto.org ,CC license

 English
English Albanian
Albanian
 Armenian
Armenian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Catalan
Catalan
 Croatian
Croatian
 Czech
Czech
 Danish
Danish
 Dutch
Dutch
 Finnish
Finnish
 French
French
 Georgian
Georgian
 German
German
 Greek
Greek
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Italian
Italian
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Macedonian
Macedonian
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Polish
Polish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Romanian
Romanian
 Russian
Russian
 Sami : Lule sami
Sami : Lule sami
 Sami : North sami
Sami : North sami
 Sami : South sami
Sami : South sami
 Scientific names
Scientific names
 Serbian
Serbian
 Spanish
Spanish
 Swedish
Swedish
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian