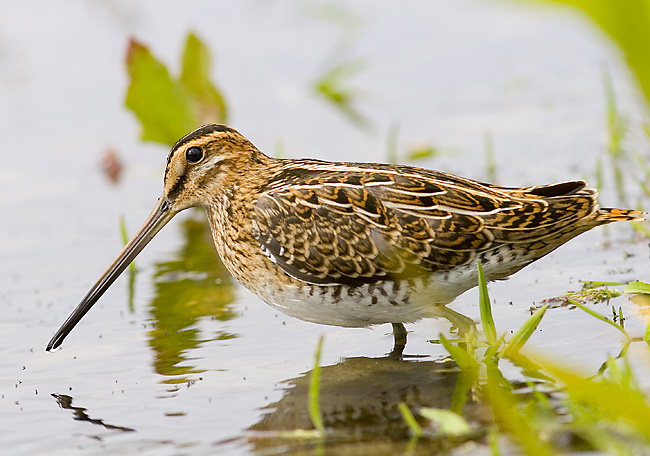
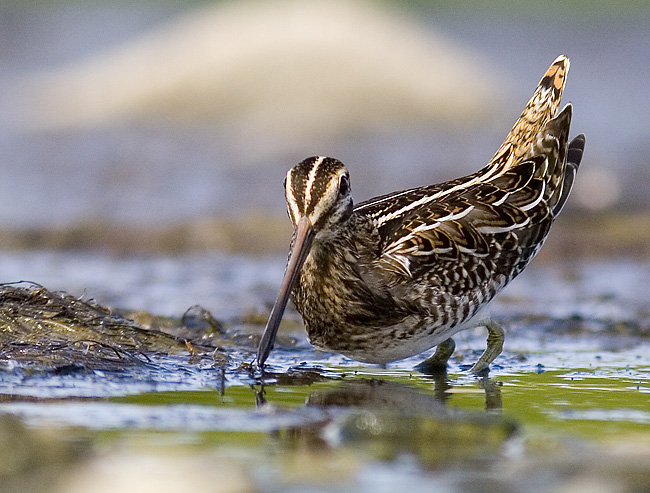
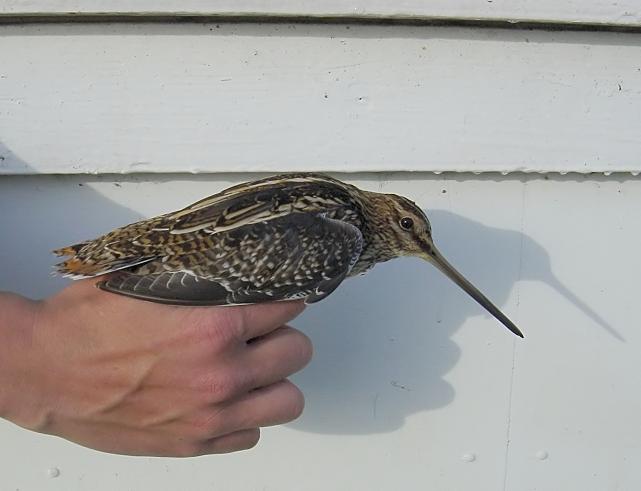
Snipe (Gallinago gallinago)
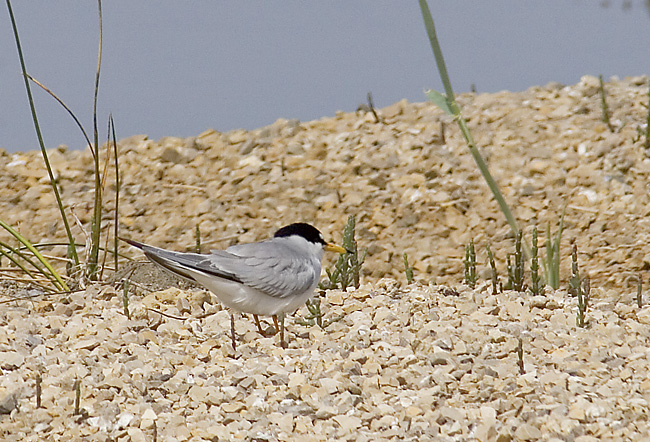
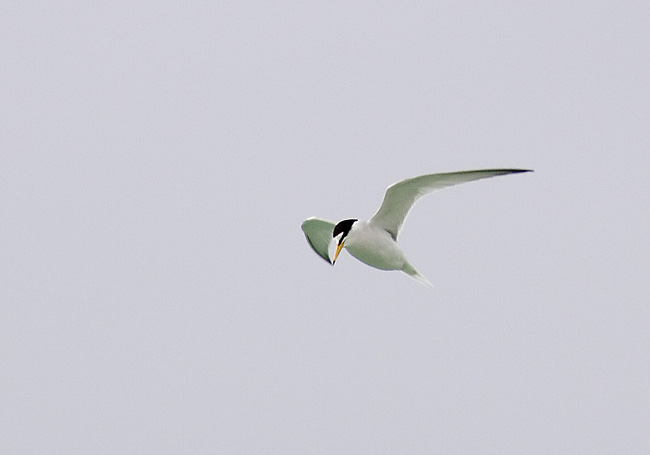
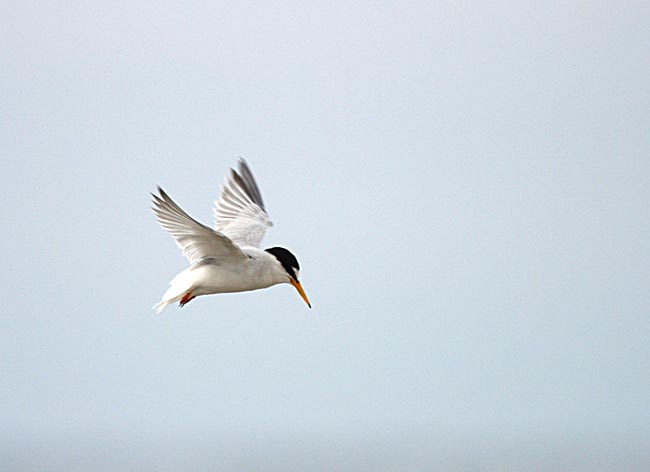
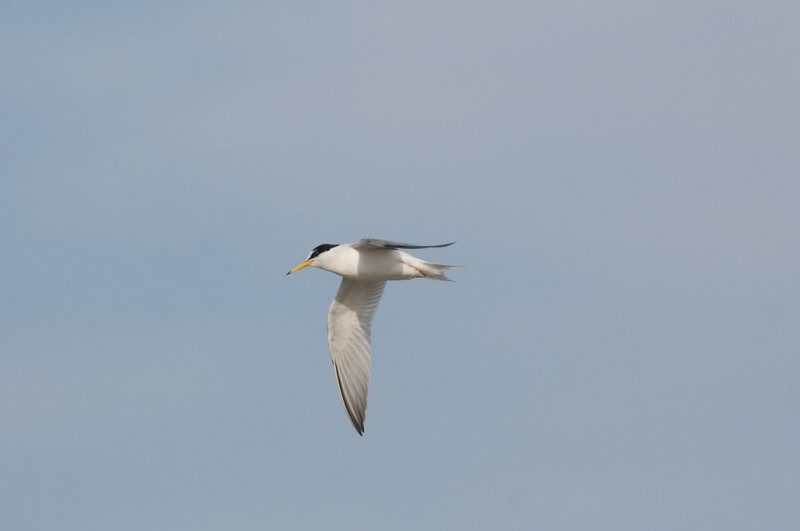
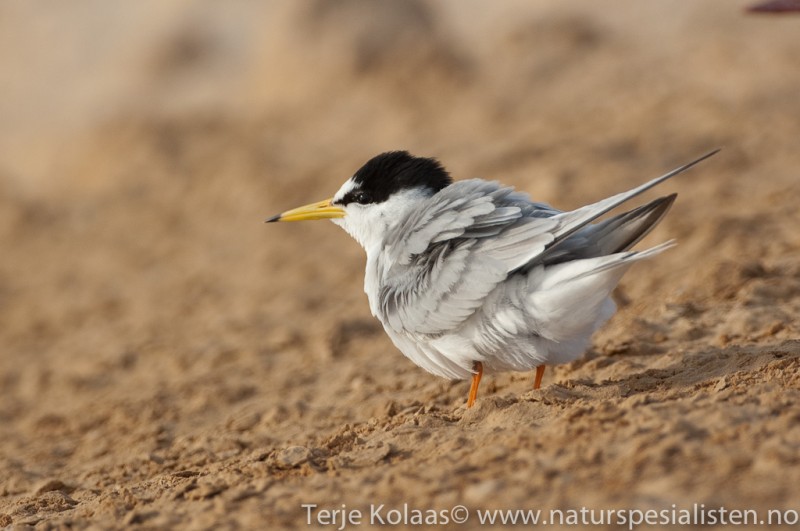
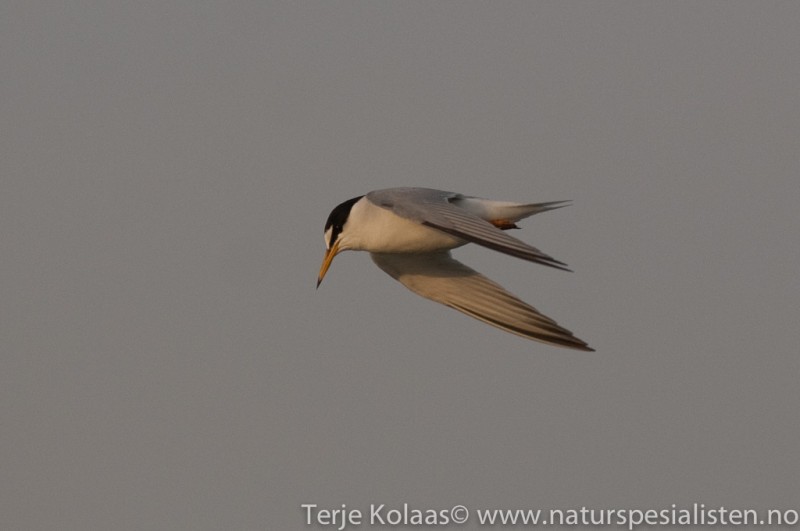
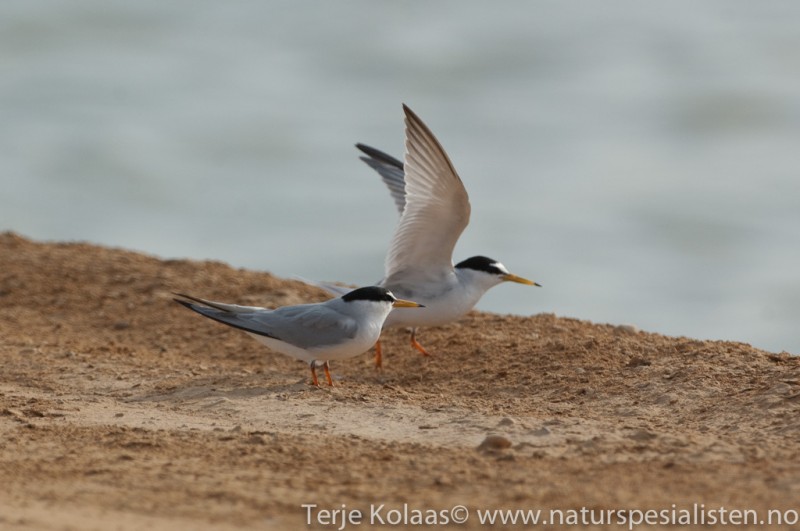
Little Tern (Sternula albifrons)
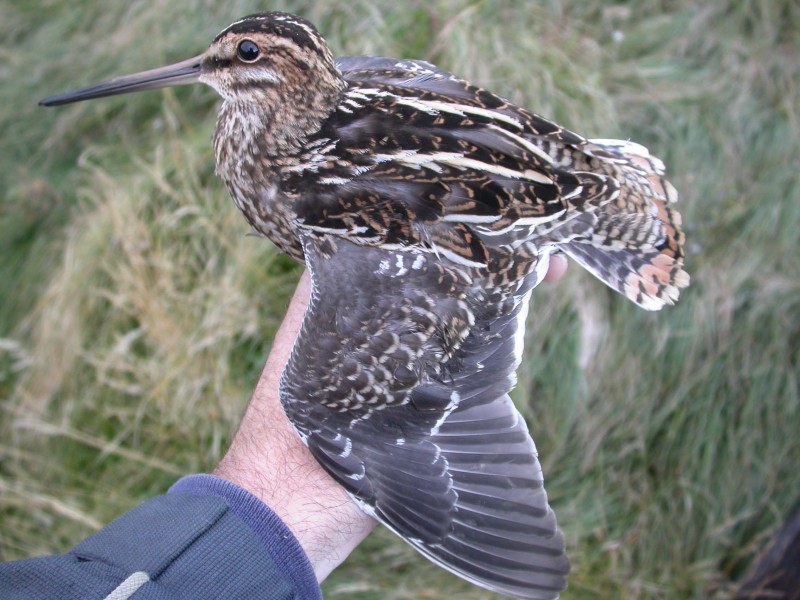
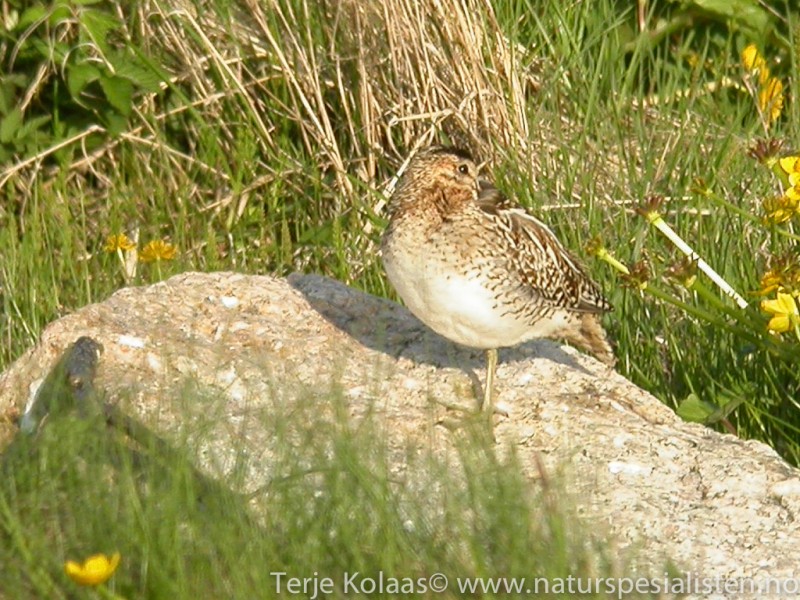
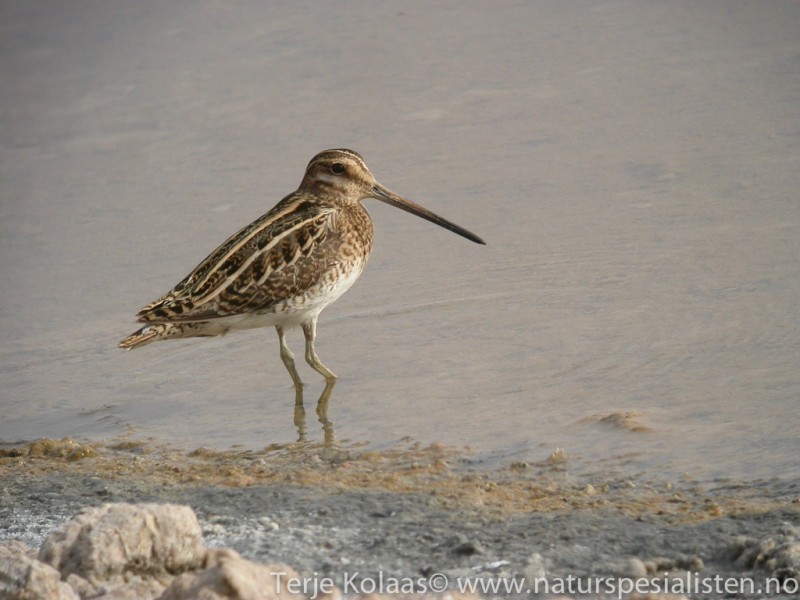
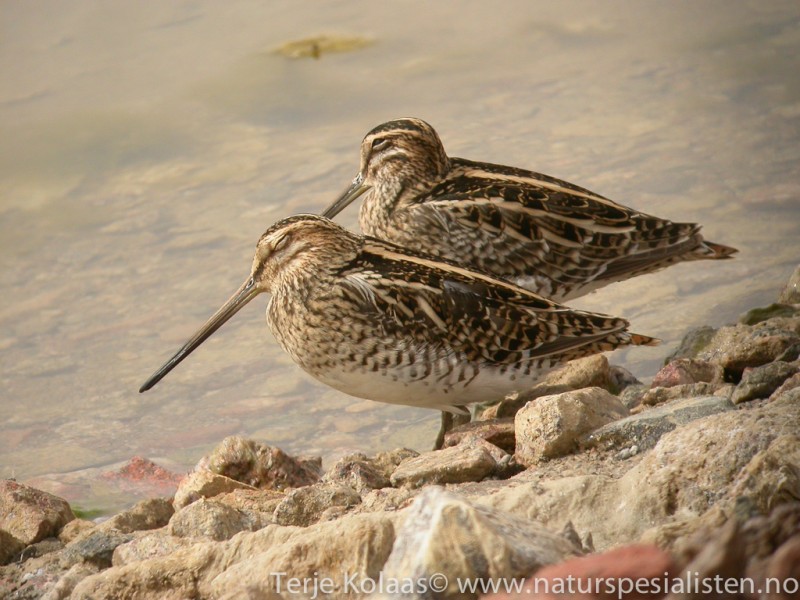
By far the most common snipe in most areas. Bill longer than congeners. Belly white, in contrast to barred flanks. Upperparts of wings with white trailing edge, underparts with white wingbars. Diagnostic escape flight when flushed, with zig-zag change of direction, characteristic call and long period of circling the area before landing (or leaving altogether).
Sound:Quite vocal, especially at breeding ground. Almost always give diagnostic hoarse and nasal "kaaat" call when flushed. Song an unmistakable bleating, drumming sound produced by vibrating tail feathers in sky-dives. Another territorial call is a rhythmic, mechanical and sharp "tika-tika-tka", or "ika-ka-ka".
Display, flush:
Distribution:
Wikipedia: map (se also Xeno-canto below)
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CCWhite forehead with white wedge above eye in all plumages. Legs, and most of bill yellow in adult breeding plumage. Very small and longwinged tern. Only 2/3 of size of Common Tern. Head and bill proportionally longer than Chlidonias species and congeners, while tail is shorter. Back paler grey and belly whiter. First primaries form a dark front edge to wing. In winter the bill darkens, legs turn a dirty yellow and the white forehead expands. Juvenile resembles adult winter, but has yellowish bill base and scale patterned back. Flight fluttering with rapid wing-beats, which together with size, is usually sufficient to determine the species.
Sound:Fairly distinct voice. Contact call a sharp "kitt", often combined to form undulating, rolling series. Not as sharp and penetrating as Common- and Arctic Tern.
Contact call:
Distribution:
Xeno-canto: map
Ecology:Birdlife ecology
Links:
Observation.org Latest observations
Image search Flickr NB! May give other species
CC
 English
English Albanian
Albanian
 Armenian
Armenian
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Catalan
Catalan
 Croatian
Croatian
 Czech
Czech
 Danish
Danish
 Dutch
Dutch
 Finnish
Finnish
 French
French
 Georgian
Georgian
 German
German
 Greek
Greek
 Hungarian
Hungarian
 Italian
Italian
 Latvian
Latvian
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian
 Macedonian
Macedonian
 Norwegian
Norwegian
 Polish
Polish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Romanian
Romanian
 Russian
Russian
 Sami : Lule sami
Sami : Lule sami
 Sami : North sami
Sami : North sami
 Sami : South sami
Sami : South sami
 Scientific names
Scientific names
 Serbian
Serbian
 Spanish
Spanish
 Swedish
Swedish
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian